One thing that can make your website look good or bad is the amount of colours you use. too many colours will make the website look messy and cluttered and also hard for the audience to get around the site, which is often the case on websites, but too little colours will make it look plain and boring. The amount of colours that will work best on the website would be three.
Primary colour
This colour will be on a lot of the website, setting the tone for the website.
Secondary colour
This colour is to back up the primary colour, It could be a shade darker or lighter than the primary colour.
Highlight colour
This colour would contrast more to the primary and secondary colours. It is used to highlight important parts of the website but not too much.
This is the colour wheel, which is helpful because it helps to understand which colours combine well.

Analogue Colours
The Analogue colour is the colours which are on either side of a given colour. A secondary colour, which is usually a shade darker or lighter than the primary colour, is most likely to be an analogue colour.

Complementary Colours
Complementary colours are directly opposite from one another, which are contrasting, making them stand out against each other in web design. These are good to use as highlight colours because the contrast makes it easy to see what you are highlighting.

Split Complementary colours
The split complementary colours are the colours next to the analogues compliment colour as the diagram shows above. These colour theory gives a high contrasting web page. However, this way is less extreme than using Complementary colours itself.
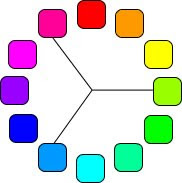
Triad colours
This colour theory is the colours equidistant from each other on the colour wheel.





















